- City Fajr Shuruq Duhr Asr Magrib Isha
- Dubai 04:31 05:49 12:21 15:48 18:47 20:05
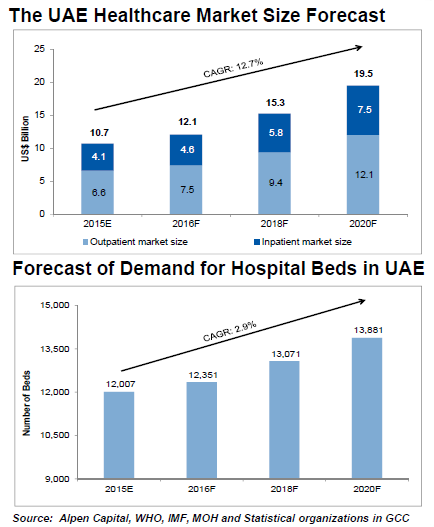
The UAE healthcare market is projected to reach $19.5 billion (Dh71.56 billion) by 2020, achieving an annual average growth of 12.7 per cent, marginally higher than the GCC growth average.
The outpatient and inpatient markets are projected to reach $12.1 billion (Dh44.4 billion) and $7.5 billion (Dh27.5 billion), respectively, in 2020. The country is likely to see an increase in demand for the number of hospital beds at nearly 3 per cent every year to reach more than 13,800 beds by 2020, according to Alpen Capital’s GCC Healthcare Industry report issued on Tuesday.
With its vision to develop world-class healthcare infrastructure, expertise, and services, the UAE government is extensively expanding and upgrading its healthcare systems to match international standards. UAE accounts for 26 per cent of the total healthcare spend by GCC governments and the per capita healthcare spending in the UAE was at $1,569 in 2013, the second highest in the GCC.
According to Alpen Capital, the GCC healthcare market is projected to grow at a 12.1 per cent CAGR from an estimated $40.3 billion in 2015 to $71.3 billion in 2020, driven by an increase in the population and rising cost of treatment.
From an estimated $24 billion in 2015, the outpatient market is forecasted to reach $42.4 billion in 2020. The inpatient market is anticipated to grow from $16.4 billion to $28.9 billion during the same period.
The healthcare market in each GCC country is anticipated to expand by 11 per cent-13 per cent between 2015 and 2020 in terms of annual average growth rates.
The demand for number of hospital beds in the GCC region is projected to grow at a 2.3 per cent CAGR from an estimated 101,797 in 2015 to 113,925 in 2020.
“Development of the healthcare sector has taken a center stage in the GCC countries, as they witness an era of demographic transition accompanied by rising prevalence of lifestyle-related diseases. In order to ease the growing pressure on the healthcare system, the GCC governments are injecting huge funds as well as encouraging private sector participation to build hospitals and clinics, upgrade the existing infrastructure, and match the quality of services offered in developed countries. They are also investing heavily in technological advancements as well as rolling out mandatory health insurance schemes in all the countries to further accelerate the growth of the healthcare sector”, said Sameena Ahmad, Managing Director, Alpen Capital.
“The GCC governments’ emphasis on the development of the healthcare sector has resulted in several investment opportunities for the private sector. Over the last year, we have seen a steady flow of private equity funds into the sector and the region has witnessed several successful M&A transactions. The GCC governments’ budgets are increasingly coming under pressure amid falling oil prices thereby opening up investment arenas for regional and international private sector players to make their entry into the healthcare market. We see this trend strengthening as governments and private companies work with each other to benefit from the opportunities presented by the GCC healthcare sector”, says Sanjay Vig, Managing Director, Alpen Capital (ME) Limited
The GCC governments’ budgets are increasingly coming under pressure amid falling oil prices. Accordingly, governments across the region are likely to curtail or defer their expenditure. A prolonged low oil price environment may influence the budgets of the GCC governments and, therefore, the healthcare spending.
The cost of medical treatments in the GCC is high compared to the developed as well as emerging medical destinations leading several local patients in the GCC to travel abroad to seek treatment. In addition to the cost disadvantage, another factor driving outbound medical tourism is limited super-specialized care in areas such as oncology and cardiology.
The GCC faces a dearth of local talent to meet the requirement at healthcare centers. Another challenging factor is the high dependence on expatriates, who consider the GCC healthcare facilities as a stepping-stone to gain experience and then seek careers in the West. The GCC Healthcare sector is likely to experience a dearth of healthcare professionals in the near term.
In the GCC healthcare sector, the private players face entry barriers such as high cost of setting up a hospital and high payback period. Healthcare providers in the GCC are looking at measures to curtail their operating costs in order to offset the impact of high capital expenditure towards constructing hospitals. The current investment climate characterized by global economic uncertainty, low oil prices, and volatility in financial markets has made investors across the globe more cautious and risk-averse. This can have a negative impact on the fund-raising ability of companies in the region to finance their healthcare projects.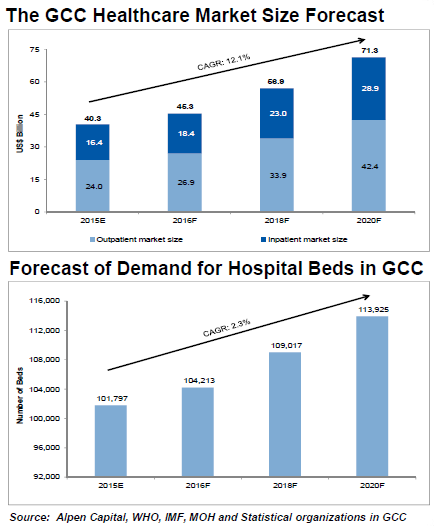
Despite a remarkable improvement in the condition of the GCC healthcare system over the last two decades, the lack of homogeneous regulations and adherence to international standards, have led to inconsistencies in the quality of services in the member nations.
Rise of the PPP model: Private sector involvement is becoming imperative to meet the rising demand for healthcare as well as to reduce the burden of costs on the government finances. Government policies to increase insurance coverage and provide other infrastructure support as well as financial incentives are drawing investors. The Government of has Dubai proposed a new PPP law to encourage private sector funding by offering them a degree of protection by structuring the tendering process and partnership contract specifications, among others. As a part of its new healthcare strategy, DHA aims to increase PPP in areas of ambulatory care, LTC, home care and day-surgery centers. Such laws and strategies are likely to increase the private sector involvement in the UAE’s healthcare sector.
Technology: The present tech-savvy generation has encouraged the use of innovative healthcare information technology such as eVisits, digitization of electronic medical records (EMR), data analytics, and mobile applications for patient engagement. The adoption of such technologies has the potential to improve the quality of care and reduce the cost substantially for both patients as well as providers.
Rising focus on preventive care: Growing health awareness among the residents along with the GCC governments’ effort to improve the basic health indicators is leading to a shift from curative care to preventive care. Focus on the prevention of diseases will not only improve the public health profile but can also help reduce healthcare expenditure and enhance the quality of care.
Long-term and post-acute care facilities (LTPAC): The rising prevalence of chronic diseases alongside an anticipated increase in the ageing population is prompting the need for long-term and post-acute care facilities in the GCC region. LTPAC facilities offer medical as well as non-medical services to patients with prolonged illness or disability that renders them incapable of taking care of themselves for a long period.
![]() Follow Emirates 24|7 on Google News.
Follow Emirates 24|7 on Google News.